Cisco Meraki Virtual MX with AWS Transit Gateway on AWS
Partner Solution Deployment Guide

February 2024
Simarbir Singh, Cisco Systems Inc.
Muffadal Quettawala, AWS Partner team
Shivansh Singh, AWS Partner Integrations Engineering

| Refer to the GitHub repository to view source files, report bugs, submit feature ideas, and post feedback about this Partner Solution. To comment on the documentation, refer to Feedback. |
This Partner Solution was created by Cisco Systems Inc. in collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS). Partner Solutions are automated reference deployments that help people deploy popular technologies on AWS according to AWS best practices. If you’re unfamiliar with AWS Partner Solutions, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide.
Overview
This guide covers the information you need to deploy the Cisco Meraki Virtual MX with AWS Transit Gateway Partner Solution in the AWS Cloud. It helps organizations connect software-defined wide area networks (SD-WANs) to applications running on AWS.
Cisco Meraki Virtual MX on AWS
Meraki vMX is a virtualized security and SD-WAN network appliance. This Quick Start deploys vMX as a node to extend the common policy, segmentation, and security of SD-WAN environments at scale. The deployment includes an active-active pair of redundant vMX appliances in a highly available configuration. With AWS Transit Gateway as a cloud router, connectivity can be scaled across virtual private clouds (VPCs) with workloads in multiple AWS Regions. You can configure, monitor, and maintain all of your Meraki devices from a single Meraki dashboard.
Costs and licenses
There is no cost to use this Partner Solution, but you will be billed for any AWS services or resources that this Partner Solution deploys. For more information, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide.
This deployment is not a warm spare configuration. It requires you to have at least two vMX licenses. If your organization has already reached its vMX license limit, you will be unable to create new vMX networks until a vMX network is deleted or additional licenses are added. For more information, see Add Another License. If you do not have access to a vMX license or require additional vMX licenses, please reach out to your Meraki reseller or sales representative.
The deployment requires a subscription to the Amazon Machine Image (AMI) for Meraki vMX, which is available from AWS Marketplace. For more information, see Deployment steps, later in this guide.
Architecture
Deploying this Quick Start for a new virtual private cloud (VPC) with default parameters builds the following Meraki VMX environment in the AWS Cloud.
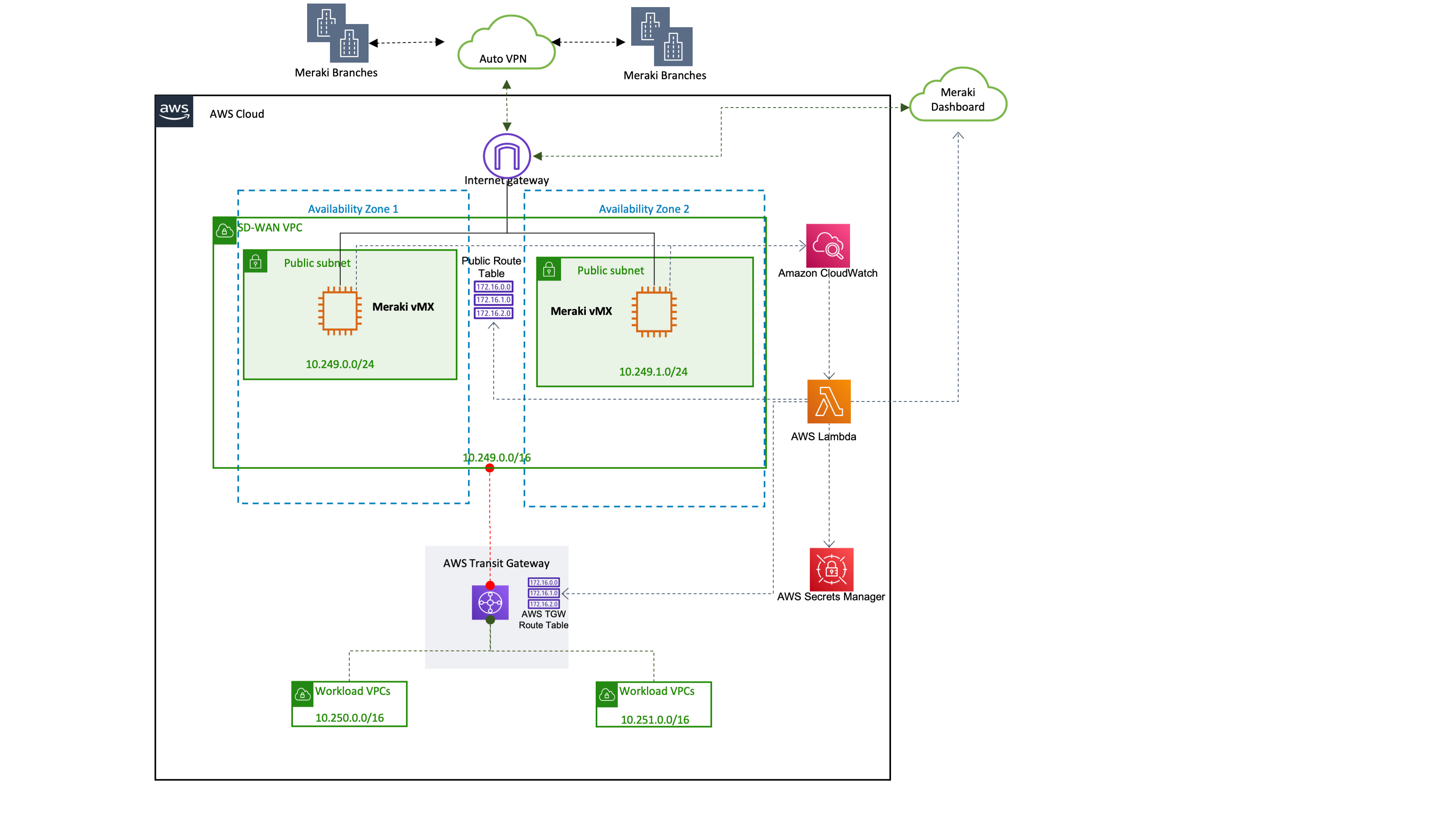
As shown in Figure 1, the Quick Start sets up the following:
-
A highly available architecture that spans two Availability Zones.*
-
A VPC configured with public and private subnets, according to AWS best practices, to provide you with your own virtual network on AWS.*
-
An internet gateway that connects the VPC to the internet.
-
A VPC route table associated with the public subnets to specify routing rules for outbound internet traffic.
-
In the public subnets, Meraki vMX appliances on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances.
-
In the private subnets, elastic network interfaces to enable traffic routing from all subnets in the Availability Zone to AWS Transit Gateway.
-
AWS Transit Gateway attached to the VPC, enabling connectivity to attached workload VPCs in other AWS Regions.
-
A transit gateway route table associated with the VPC for routing rules to AWS Transit Gateway.
-
Amazon CloudWatch to collect logs of vMX instance performance.
-
AWS Lambda to monitor the state of the vMX instances. If an instance fails, AWS Lambda updates route tables to point to a healthy instance and logs the event in CloudWatch.
-
AWS Secrets Manager to store a Meraki API key. AWS Lambda uses the API key to access the Meraki dashboard when updating route tables.
*The template that deploys the Quick Start into an existing VPC skips the components marked by asterisks and prompts you for your existing VPC configuration.
Deployment options
This Partner Solution provides the following deployment options:
-
Deploy Meraki VMX into a new VPC. This option builds a new AWS environment that consists of the VPC, subnets, NAT gateways, security groups, bastion hosts, and other infrastructure components. It then deploys Meraki VMX into this new VPC.
-
Deploy Meraki VMX into an existing VPC. This option provisions Meraki VMX in your existing AWS infrastructure.
This Partner Solution provides separate templates for these options. It also lets you configure Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) blocks, instance types, and Meraki VMX settings.
Predeployment steps
Subscribe to the Meraki vMX AMI
This deployment requires a subscription to the AMI for Meraki vMX in AWS Marketplace.
-
Sign in to your AWS account.
-
Open the page for the Cisco Meraki vMX AMI in AWS Marketplace, and then choose Continue to Subscribe.
-
Review the terms and conditions for software usage, and then choose Accept Terms. A confirmation page loads, and an email confirmation is sent to the account owner. For detailed subscription instructions, see the AWS Marketplace documentation.
-
When the subscription process is complete, exit out of AWS Marketplace without further action. Do not provision the software from AWS Marketplace—the Quick Start deploys the AMI for you.
Meraki dashboard configuration
Before deploying, do the following:
-
Complete the instructions in the "Meraki Dashboard Configuration" section of the vMX Setup Guide for Amazon Web Services (AWS). During configuration, you generate authentication tokens for the vMX appliances. Copy and save the tokens. You must enter them in the vMX1Token and vMX2Token parameters in the AWS CloudFormation console during Quick Start deployment.
-
Set network tags vMX-1 and vMX-2 to identify vMX nodes as the primary and secondary hub, respectively. To set network tags in the Meraki dashboard, see Manage Tags.
-
Configure your branch sites as Meraki Auto VPN spokes with the vMX instances as the primary and secondary hubs. For more information, see Meraki Auto VPN - Configuration and Troubleshooting.
Deployment steps
-
Sign in to your AWS account, and launch this Partner Solution, as described under Deployment options. The AWS CloudFormation console opens with a prepopulated template.
-
Choose the correct AWS Region, and then choose Next.
-
On the Create stack page, keep the default setting for the template URL, and then choose Next.
-
On the Specify stack details page, change the stack name if needed. Review the parameters for the template. Provide values for the parameters that require input. For all other parameters, review the default settings and customize them as necessary. When you finish reviewing and customizing the parameters, choose Next.
Unless you’re customizing the Partner Solution templates or are instructed otherwise in this guide’s Predeployment section, don’t change the default settings for the following parameters: QSS3BucketName,QSS3BucketRegion, andQSS3KeyPrefix. Changing the values of these parameters will modify code references that point to the Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket name and key prefix. For more information, refer to the AWS Partner Solutions Contributor’s Guide. -
On the Configure stack options page, you can specify tags (key-value pairs) for resources in your stack and set advanced options. When you finish, choose Next.
-
On the Review page, review and confirm the template settings. Under Capabilities, select all of the check boxes to acknowledge that the template creates AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) resources that might require the ability to automatically expand macros.
-
Choose Create stack. The stack takes about 15 minutes to deploy.
-
Monitor the stack’s status, and when the status is CREATE_COMPLETE, the Cisco Meraki Virtual MX with AWS Transit Gateway deployment is ready.
-
To view the created resources, choose the Outputs tab.
Postdeployment steps
After deployment, you must do the following:
-
Attach the workload VPCs to the transit gateway. For more information, see Transit gateway attachments to a VPC.
-
Update the VPC route table for the workload subnets. For more information, see Add and remove routes from a route table.
vMX HA architecture
The deployment architecture is fault tolerant with two vMX instances in different Availability Zones. An AWS Lambda function handles instance-level failures by checking the state of vMX EC2 instances. For software-level failures, it checks the vMX health state on the Meraki VMX dashboard. In the case of a vMX instance failure, the AWS Lambda function logs the error in CloudWatch and updates the VPC and transit gateway routes to point to a healthy instance.
To recover a failed Meraki vMX instance
-
Sign in to the Meraki dashboard.
-
Generate a new authentication token for the failed instance. For more information, see step 4 in the Meraki Dashboard Configuration section, previously in this guide.
-
Deploy a new vMX stack. For deployment links, see Launch the Quick Start, previously in this guide. On the Specify Stack Details page in the CloudFormation console, specify the following parameters:
-
InstanceType. Choose the same Amazon EC2 instance type that you specified during the previous deployment. -
KeyPairName. Enter the name of an existing EC2 key pair. -
SubnetID. Select the SubnetID to deploy the vMX instance. -
vMXNetworkTag. Specify the network tag associated with the vMX instance on the Meraki dashboard. -
vMXToken. Enter the new authentication token generated from the Meraki dashboard.
-
Best practices for using Meraki VMX on AWS
For best practices, see vMX Setup Guide for Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Troubleshooting
For troubleshooting common Partner Solution issues, refer to the AWS Partner Solution General Information Guide and Troubleshooting CloudFormation.
Customer responsibility
After you deploy a Partner Solution, confirm that your resources and services are updated and configured—including any required patches—to meet your security and other needs. For more information, refer to the Shared Responsibility Model.
Feedback
To submit feature ideas and report bugs, use the Issues section of the GitHub repository for this Partner Solution. To submit code, refer to the Partner Solution Contributor’s Guide. To submit feedback on this deployment guide, use the following GitHub links:
Notices
This document is provided for informational purposes only. It represents current AWS product offerings and practices as of the date of issue of this document, which are subject to change without notice. Customers are responsible for making their own independent assessment of the information in this document and any use of AWS products or services, each of which is provided "as is" without warranty of any kind, whether expressed or implied. This document does not create any warranties, representations, contractual commitments, conditions, or assurances from AWS, its affiliates, suppliers, or licensors. The responsibilities and liabilities of AWS to its customers are controlled by AWS agreements, and this document is not part of, nor does it modify, any agreement between AWS and its customers.
The software included with this paper is licensed under the Apache License, version 2.0 (the "License"). You may not use this file except in compliance with the License. A copy of the License is located at https://aws.amazon.com/apache2.0/ or in the accompanying "license" file. This code is distributed on an "as is" basis, without warranties or conditions of any kind, either expressed or implied. Refer to the License for specific language governing permissions and limitations.